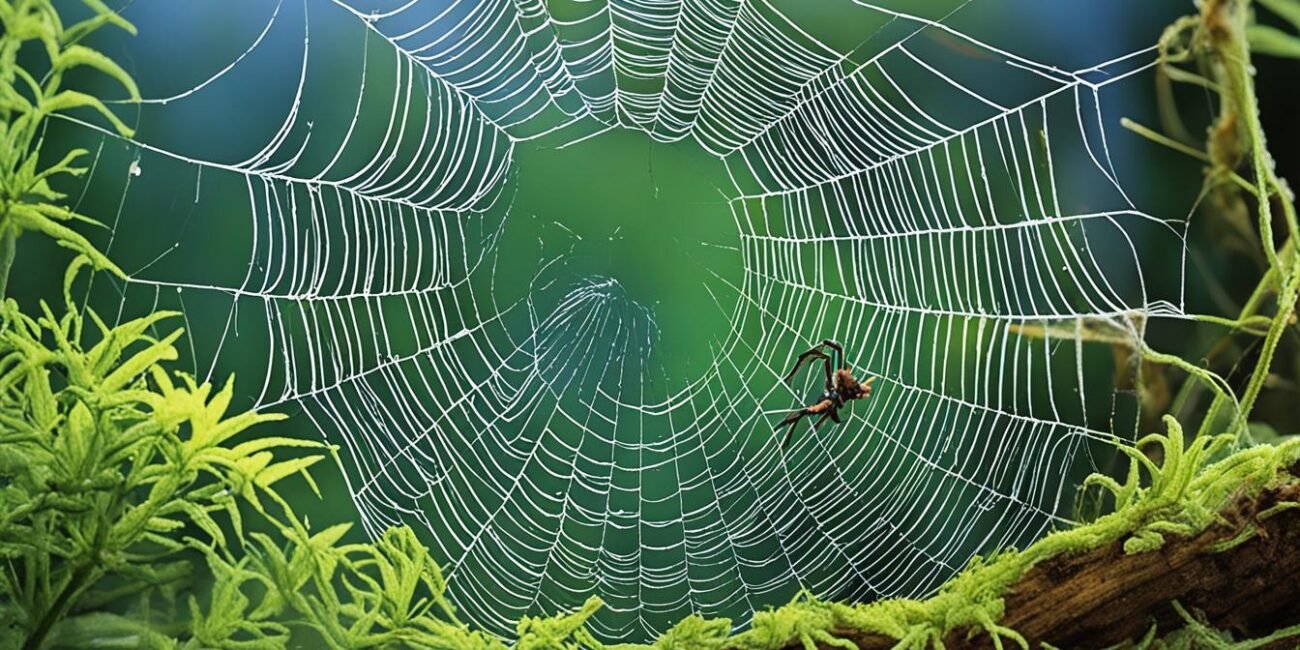
Welcome to our fascinating journey into the diverse habitats of spiders. In this article, we will delve into the natural habitat of spiders and discover their unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in various environments. From spider nesting grounds to the intricate locations of spider webs, we will explore the spider-friendly environments that support their existence. So let us begin our exploration of these remarkable creatures and the conditions that make up their ideal living spaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Spider habitats are diverse and vary depending on the species and their specific adaptations.
- Understanding the diversity and adaptation of spiders in different environments is crucial to understanding their survival strategies.
- Spider nesting grounds and the locations of spider webs play a significant role in their habitat.
- Spiders thrive in spider-friendly environments that offer suitable living conditions.
- The exploration of spider habitats unveils the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Spider Design and Body Size
Spiders have evolved to thrive in diverse terrestrial environments. Their remarkable design and body size are critical factors in their ability to adapt and survive in various habitats. The interplay between their physique, adaptations, and physiological variability enables spiders to navigate and excel in their surroundings.
One of the fundamental aspects of spider design is their body size. The size of a spider’s body determines its surface-to-volume ratio, which has essential implications for its physiological functions. Large spiders typically have a lower surface-to-volume ratio, allowing them to conserve moisture and energy more efficiently. On the other hand, small spiders possess a higher surface-to-volume ratio, which aids in their ability to absorb oxygen and nutrients through their thin exoskeleton.
Spider body size also influences their metabolic rate, influencing their energy requirements and activity levels. Smaller spiders generally have higher metabolic rates and require more frequent feeding to support their physiological demands. Conversely, larger spiders have lower metabolic rates, enabling them to survive on fewer prey items over longer periods.
Spider body size plays a crucial role in their ability to survive in different habitats. The interplay between their surface-to-volume ratio, metabolic rate, and energy costs contributes to their physiological and adaptive characteristics.
In addition to body size, spider design encompasses an array of adaptations that facilitate their survival. Spiders exhibit an astounding variety of anatomical structures and physiological mechanisms that allow them to capture prey, defend themselves, and thrive in their surroundings.
For example, the iconic web-building spiders possess specialized spinnerets that produce silk threads of different types and strengths. These webs serve multiple purposes, from ensnaring prey to communication and shelter. Other spiders have evolved unique hunting strategies, such as ambush or jumping techniques, highlighting the incredible diversity of adaptations among spider species.
The complex interplay between spider design, body size, and adaptations contributes to their remarkable physiological variability. Each spider species has evolved specific features that enhance their chances of survival in their respective habitats. The adaptability of spiders is truly awe-inspiring, allowing them to thrive in a wide range of ecosystems across the globe.
Spider Adaptations to Terrestrial Environments
Spiders have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in terrestrial environments, allowing them to overcome the challenges presented by temperature fluctuations, humidity, and water regulation. These adaptations, combined with their small body size and specialized structures, enable spiders to survive and thrive in a variety of climates.
One example of a spider adaptation to terrestrial environments is the gray hair of the Goliath birdeater (Theraphosa blondi). This large tarantula species uses its coarse hairs as a defense mechanism against predators. The gray hairs create the appearance of larger size, serving as a deterrent to potential threats.
The Brazilian wandering spider (Phoneutria) showcases another notable adaptation. This spider has developed venomous bites as a means of hunting and self-defense. The venom is potent and can cause severe pain and even paralysis in its prey or predators.
Spiders also rely on their ability to regulate their own body temperature in changing environments. Their small body size allows for effective heat exchange and quick adaptation to temperature fluctuations. By being ectothermic creatures, spiders can adjust their metabolic rates to match environmental conditions, enabling them to conserve energy when necessary.
Furthermore, spiders possess specialized structures that aid in water regulation. Unlike most terrestrial animals, spiders are not equipped with internal water storage systems. Instead, they have evolved efficient mechanisms to conserve and obtain water. Some species have a specialized structure called the scopula that allows them to extract moisture from surfaces such as leaves or walls. Others may employ the behavior of drinking droplets from their own silk webs.
All these adaptations enable spiders to thrive in a wide range of terrestrial environments, from humid rainforests to arid deserts. Their ability to navigate and adapt to these diverse habitats showcases the remarkable resilience and ingenuity of these arachnids.
Spider Adaptations Key Points:
- Spiders have evolved unique adaptations to overcome challenges in terrestrial environments.
- Goliath birdeater has gray hair for defense against predators.
- Brazilian wandering spider has venomous bites for hunting and defense.
- Spiders regulate body temperature through their small body size and metabolic adaptations.
- Specialized structures help spiders regulate water in their environment.
Rare Spider Species in the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest is an incredible ecosystem that is home to a wide variety of spider species. In this section, we will explore some of the rare and fascinating spiders that can be found in this biodiverse region.
Goliath Birdeater
One of the most famous spider species in the Amazon Rainforest is the Goliath birdeater (Theraphosa blondi). As the largest spider in the world, it can have a leg span of up to 11 inches and is known for its impressive size and appearance. Despite its name, the Goliath birdeater primarily preys on insects, but it is capable of capturing small birds and rodents if the opportunity arises.
Brazilian Wandering Spider
The Brazilian wandering spider (Phoneutria) is another remarkable spider species found in the Amazon Rainforest. It is known for its distinctive yellow coloring and venomous bites, which can be dangerous to humans. This highly adaptable spider is often found wandering on the forest floor, hence its name, and is known for its aggressive behavior.
Pink Toe Tarantula
The pink toe tarantula (Avicularia avicularia), also known as the Guyana pinktoe, is a visually striking spider species found in the Amazon Rainforest. It gets its name from the unique pink coloration on its toes, which contrasts beautifully with its black and brown body. The pink toe tarantula is arboreal, meaning it spends its time in trees and builds elaborate webs high above the forest floor.
“The Amazon Rainforest is a treasure trove of rare spider species, showcasing the incredible diversity and adaptations that exist in nature.” – Spider enthusiast
Unusual Spider Species with Intricate Designs
When it comes to unusual traits and intricate designs, some spider species truly stand out. Let’s take a closer look at a few of these fascinating arachnids:
The Peacock Spider
The peacock spider, native to Australia, is renowned for its vibrant and mesmerizing courtship displays. The males of this species have evolved an incredible ability to perform intricate dances, showcasing flashy colors and intricate leg movements to attract potential mates. The combination of their striking appearance and unique courtship behavior makes the peacock spider a remarkable sight to behold.
The Goliath Birdeater
The goliath birdeater, officially known as Theraphosa blondi, holds the title for being the largest spider in the world. With a leg span of up to 11 inches, this massive spider resides in the rainforests of South America. While its size alone is impressive, it also possesses unique traits such as powerful fangs and long, thick hairs that act as a defense mechanism against predators. Despite its intimidating features, the goliath birdeater is generally harmless to humans.
The Mirror Spider
The mirror spider, commonly found in Australia, is known for its incredible ability to camouflage amongst its surroundings. This fascinating spider has a highly reflective abdomen that mirrors its environment, making it almost invisible to predators and unsuspecting prey. The mirror spider’s unique adaptation allows it to blend seamlessly into its surroundings, ensuring its survival in the harsh Australian landscape.
In conclusion, these unusual spider species with their unique traits and intricate designs showcase the incredible diversity and adaptability of arachnids. From the peacock spider’s mesmerizing courtship displays to the goliath birdeater’s size and the mirror spider’s camouflaging ability, these arachnids continue to intrigue and captivate us with their remarkable characteristics.
Diverse Spider Species Around the World
Spider species are found in diverse regions worldwide, each contributing to the global tapestry of arachnid life. These fascinating creatures have adapted to thrive in a variety of unique environments, showcasing their incredible resilience and evolutionary prowess.
The Golden Orb-Weaver Spider
One notable species is the golden orb-weaver spider, commonly found in Southeast Asia and Australia. What sets this spider apart is its striking bright yellow coloration, which adds a touch of vibrancy to the natural world. Apart from its aesthetic appeal, the golden orb-weaver plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by capturing insects in its large, intricate webs.
The Pink Toe Tarantula
Another intriguing spider species is the pink toe tarantula, native to South America. This delightful creature has gained popularity among arachnid enthusiasts as a beloved pet. The pink toe tarantula derives its name from its distinctive pink-colored feet, adding a touch of uniqueness to its appearance. Known for its docile temperament, it is considered one of the more manageable tarantula species to keep as pets.
These diverse spider species exemplify the remarkable adaptability of arachnids and their ability to carve out niches in different corners of the world. Each species contributes to the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, highlighting the incredible diversity and beauty of nature.
Marvels of Evolution: One-of-a-Kind Spider Species
When it comes to the incredible diversity of spider species, some stand out as true marvels of evolution. These unique creatures have developed fascinating adaptations and behaviors that set them apart from the rest. In this section, we will explore four one-of-a-kind spider species that showcase the wonders of evolution: the Gooty Tarantula, Peacock Spider, Ogre-Faced Spider, and Net-Casting Spider.
Gooty Tarantula
The Gooty Tarantula, also known as the Metallic Tarantula, is a visually stunning spider native to the forests of India. Its vibrant blue coloration is an extraordinary adaptation that aids in camouflage and deterrence. This unique color sets the Gooty Tarantula apart from other spider species, making it a true natural wonder.
Peacock Spider
The Peacock Spider, found primarily in Australia, is renowned for its mesmerizing dance moves. During courtship, the male Peacock Spider performs an intricate mating dance, showcasing its vibrant colors and intricate patterns. This elaborate display is a testament to the power of natural selection and sexual selection in evolution.
Ogre-Faced Spider
The Ogre-Faced Spider, also known as the Net-Casting Spider, possesses a fascinating adaptation that allows it to deceive both prey and predators. This spider builds a web that resembles a fallen leaf suspended between its front legs, creating a camouflaged trap. When prey approaches, the Ogre-Faced Spider releases the web, ensnaring its unsuspecting victim. This remarkable behavior demonstrates the complexity of evolutionary strategies for survival.
Net-Casting Spider
The Net-Casting Spider, a master of disguise and deception, constructs a unique web-like trap to capture its prey. This spider holds a small rectangular web between its front legs, similar to a fishing net, and uses its strong eyesight to locate passing insects. When the moment is right, the Net-Casting Spider swiftly lunges forward with its web, capturing its prey in a matter of milliseconds. This extraordinary hunting technique is a testament to the diverse and intricate adaptations that have evolved among spider species.
These one-of-a-kind spider species, with their unique adaptations and behaviors, provide a glimpse into the marvels of evolution. From the vibrant blue of the Gooty Tarantula to the intricate dance moves of the Peacock Spider, each species has its own captivating story to tell. As we continue to study these remarkable creatures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the extraordinary diversity and complexity of the natural world.
| Spider Species | Notable Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Gooty Tarantula | Vibrant blue coloration for camouflage and deterrence |
| Peacock Spider | Intricate mating dance with vibrant colors and patterns |
| Ogre-Faced Spider | Web disguised as a fallen leaf to deceive prey and predators |
| Net-Casting Spider | Web-like trap resembling a fishing net to capture prey |
The Wonders of Distinct Spider Species
Distinct spider species offer profound insights into the intricate workings of nature. Each species possesses unique characteristics and abilities that contribute to the diverse tapestry of spider life. Let’s explore some fascinating examples:
Zebra Spider (Salticus scenicus)
The zebra spider, also known as the jumping spider, captivates with its agility and impressive jumping abilities. With keen eyesight and sharp reflexes, these small spiders can accurately gauge distances and pounce on their prey with astonishing speed. Their vibrant black and white striped patterns add to their charm.
Spiny Orb-Weaver (Gasteracantha canciformis)
The spiny orb-weaver stands out with its striking appearance and unique defense mechanisms. This small spider features sharp spines on its abdomen, which serve as a deterrent to predators and aid in prey capture. Their intricate orb-shaped webs, adorned with stabilimenta, are masterfully crafted and enable efficient hunting.
Orchid Spider (Leucauge magnifica)
The orchid spider stands apart with its colorful and captivating appearance. Adorned with vibrant hues of yellow, orange, and green, these delicate spiders blend seamlessly with the flowers they inhabit. As ambush predators, they patiently wait for unsuspecting insects to approach, capitalizing on their floral camouflage.
Diving Bell Spider (Argyroneta aquatica)
The diving bell spider is an extraordinary species that demonstrates adaptation to an aquatic lifestyle. Found in freshwater habitats, these spiders build underwater domes known as “diving bells” from silk and foliage. These structures provide an oxygen-rich environment where the spider can reside and capture its aquatic prey.
Desert Tarantula (Aphonopelma chalcodes)
The desert tarantula is a desert-dwelling spider renowned for its resilience in extreme arid conditions. These large and robust spiders have evolved physiological adaptations that enable them to conserve water and thrive in harsh desert environments. Their burrows provide shelter from the scorching sun, ensuring their survival.
A Closer Look at the Wonders of Distinct Spider Species:
| Spider Species | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|
| Zebra Spider | Agility and impressive jumping abilities; vibrant black and white stripes |
| Spiny Orb-Weaver | Sharp spines on the abdomen for defense and prey capture; intricate orb-shaped webs |
| Orchid Spider | Colorful appearance; floral camouflage for ambush predation |
| Diving Bell Spider | Adaptation to aquatic lifestyle; underwater silk domes for creating an oxygen-rich environment |
| Desert Tarantula | Resilience in arid conditions; physiological adaptations for water conservation |
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring spider habitats reveals the diversity and adaptation of these remarkable creatures. Each spider species is uniquely suited to its environment, showcasing the wonders of nature’s designs. From rare and unusual species like the Goliath birdeater and Brazilian wandering spider, to distinct spiders like the zebra spider and spiny orb-weaver, each one has evolved specific traits and behaviors that help them survive and thrive.
By studying spider habitats, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world. The Amazon Rainforest, with its rich biodiversity, is home to some of the most fascinating spider species on the planet. In addition, spiders from different regions such as Southeast Asia, Australia, and South America offer a global tapestry of diversity.
From spider adaptations to terrestrial environments, where temperature fluctuations and humidity pose challenges, to the marvels of evolution displayed by spiders like the Gooty Tarantula and Peacock Spider, there is endless fascination in the world of spiders. Understanding their habitats not only allows us to better understand their survival strategies, but also helps us appreciate the intricate workings of nature.
FAQ
What is the ideal spider habitat?
The ideal spider habitat varies depending on the species. However, spiders generally thrive in environments with ample food supply, suitable temperature and humidity conditions, and adequate shelter for nesting and web building.
Where are common spider habitats found?
Common spider habitats can be found in a variety of locations, including forests, grasslands, meadows, gardens, deserts, caves, and even human-made structures like houses and buildings.
What are suitable spider living conditions?
Suitable spider living conditions include a sufficient supply of insect prey, moderate temperatures, moderate humidity levels, and access to locations where they can build their webs or create nests.
Where do spiders build their webs?
Spiders build their webs in locations where they can capture their prey efficiently. Common web locations include trees, bushes, tall grass, corners of buildings, and other secluded areas where insects are abundant.
What are spider-friendly environments?
Spider-friendly environments provide ample food sources, minimal disturbances, and suitable climate conditions. These environments allow spiders to establish their nests, build their webs, and carry out their usual behaviors without unnecessary hindrances.
What are spider nesting grounds?
Spider nesting grounds are areas where spiders establish their nests or shelters. These locations can vary depending on the species and may include crevices in rocks, leaf litter, burrows in the ground, or specific plants or structures suitable for web construction.
What are some common spider habitats in urban areas?
In urban areas, spiders can often be found in gardens, parks, vacant lots, and even inside buildings. They may inhabit structures such as sheds, garages, and basements, where they can find suitable nesting spaces and access to prey.
How can I create a spider-friendly environment in my garden?
To create a spider-friendly environment in your garden, you can provide a diverse range of plants, which will attract insects for spiders to feed on. Avoid using excessive pesticides and maintain a suitable level of vegetation where spiders can build their webs.
What should I do if I find spiders in my house?
If you find spiders in your house and are comfortable with their presence, it is best to leave them be as they can help control the population of other pests. However, if you prefer not to coexist with spiders, you can carefully remove them using a cup and piece of paper or call a professional pest control service.









No Comment! Be the first one.